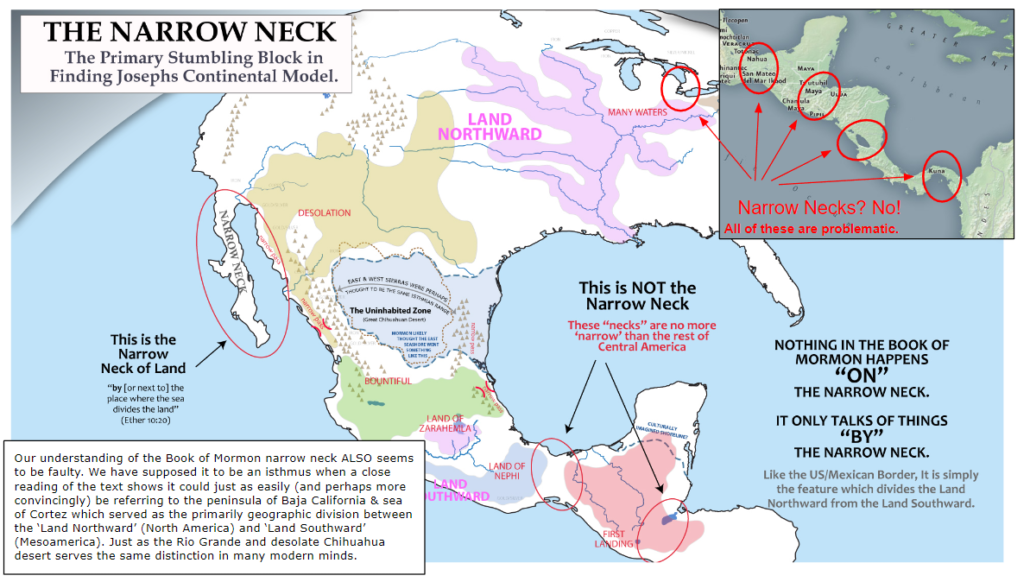
The Narrow Neck as Baja and the Sea of Cortez
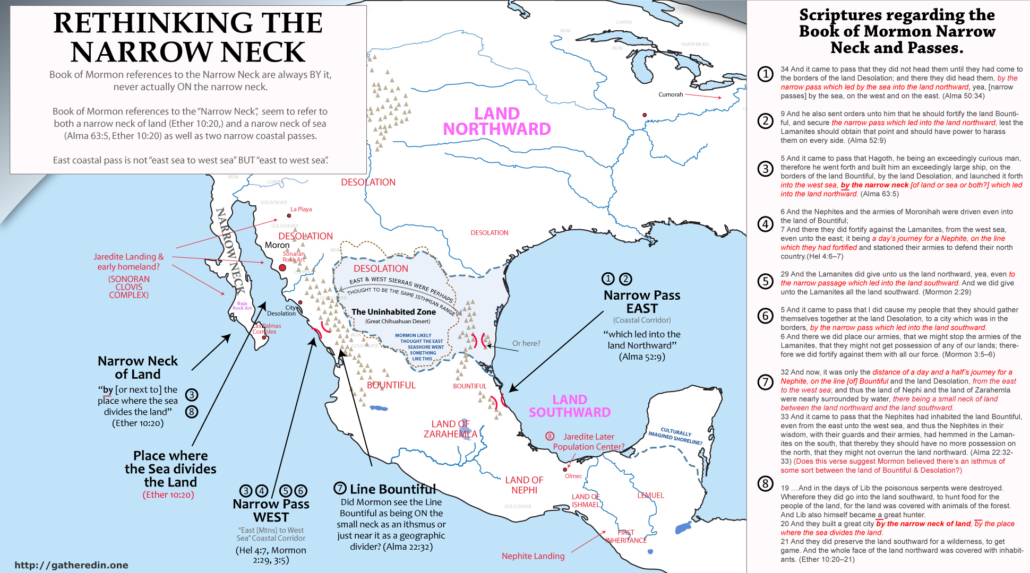
Book of Mormon accounts are always “BY” the narrow neck, never ON the narrow neck.
“Where the sea divides the land”, NOT where the land divides the sea
Narrow Passes are never said to be ON the narrow neck .

Summary: all Book of Mormon references to the narrow neck & passes
NARROW PASSES
34 And it came to pass that [Moroni] did not head [Morianton] until they had come to the borders of the land Desolation; and there they did head them, by the narrow pass which led by the sea into the land northward, yea, by the sea, on the west and on the east. (Alma 50:34)9 And [Moroni] also sent orders unto [Teancum] that he should fortify the land Bountiful, and secure the narrow pass which led into the land northward, lest the Lamanites should obtain that point and should have power to harass them on every side. (Alma 52:9)
6 And the Nephites and the armies of Moronihah were driven even into the land of Bountiful; 7 And there they did fortify against the Lamanites, from the west sea, even unto the east [sea or mountain?]; it being a day’s journey for a Nephite, on the line which they had fortified and stationed their armies to defend their north country.(Hel 4:6–7)
29 And the Lamanites did give unto us the land northward, yea, even to the narrow passage which led into the land southward. And we did give unto the Lamanites all the land southward. (Mormon 2:29)
5 And it came to pass that I did cause my people that they should gather themselves together at the land Desolation, to a city which was in the borders, by the narrow pass which led into the land southward. 6 And there we did place our armies, that we might stop the armies of the Lamanites, that they might not get possession of any of our lands; therefore we did fortify against them with all our force. (Mormon 3:5–6)
NARROW NECK
5 And it came to pass that Hagoth, he being an exceedingly curious man, therefore he went forth and built him an exceedingly large ship, on the borders of the land Bountiful, by the land Desolation, and launched it forth into the west sea, by the narrow neck which led into the land northward. (Alma 63:5)30 And it bordered upon the land which they called Desolation, it being so far northward that it came into the land which had been peopled and been destroyed, of whose bones we have spoken, which was discovered by the people of Zarahemla, it being the place of their first landing. 31 And they came from there up into the south wilderness. Thus the land on the northward was called Desolation, and the land on the southward was called Bountiful, it being the wilderness which is filled with all manner of wild animals of every kind, a part of which had come from the land northward for food. 32 And now, it was only the distance of a day and a half’s journey for a Nephite, on the line Bountiful and the land Desolation, from the east to the west sea; and thus the land of Nephi and the land of Zarahemla were nearly surrounded by water, there being a small neck of land between the land northward and the land southward. 33 And it came to pass that the Nephites had inhabited the land Bountiful, even from the east unto the west sea, and thus the Nephites in their wisdom, with their guards and their armies, had hemmed in the Lamanites on the south, that thereby they should have no more possession on the north, that they might not overrun the land northward. (Alma 22:32–33)
19 …And in the days of Lib the poisonous serpents were destroyed. Wherefore they did go into the land southward, to hunt food for the people of the land, for the land was covered with animals of the forest. And Lib also himself became a great hunter. 20 And they built a great city by the narrow neck of land, by the place where the sea divides the land. 21 And they did preserve the land southward for a wilderness, to get game. And the whole face of the land northward was covered with inhabitants. (Ether 10:20–21)
.
Overview
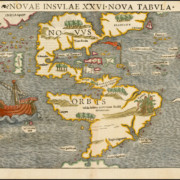
I believe many of the best correlations between the Book of Mormon’s internal geography and modern archaeological findings have been missed or passed over by Book of Mormon geographers almost exclusively because of misunderstandings surrounding the ‘Narrow Neck of Land’ mentioned in the text. Although it’s easy to see how the language of Alma 22 may give the impression that the ‘narrow passes’ mentioned in the Book of Mormon are ON the narrow neck which an isthmus separating the Land Northward & Southward– a close examination of the text allows for a different unique interpretation. In this article, we’ll go through each verse relating to the Book of Mormon narrow neck to make a case that it is actually the Baja California peninsula, which in ancient times, and even among early Spanish authors, served as the predominate geographic delineator between the inhabitants of the ‘Bountiful’ and ‘Desolate’ narrow passes of Sinaloa and Sonora west Mexico. Much the same way as the Rio Grande river and Sonoran desert serves as the main delineator between the United States and Mexico in our day. Following are just a few of the reasons why a correlation between the narrow neck and the Baja peninsula seem to be the best fit to the text.
- Joseph Smith seems to have believed that the land of Desolation was the desert Southwest & Eastern plains areas of the United States with Bountiful & Zarahemla in Meso/Central America (see this article). Since Desolation bordered the narrow neck, ONLY a Baja Narrow Neck can makes his model work!
- Not a single occurrence in the Book of Mormon is said to happen ON the narrow neck. Instead all mentions of it are in regard to being BY the narrow neck. (see Alma 50:34, Alma 63:5, Mormon 3:5–6, Ether 10:20). Not a SINGLE verse in the Book of Mormon references Bountiful or Desolation as being ON the Narrow Neck, which we would expect if traditional Tehuantepec models were correct.
- The language in Ether 10:20 (and possibly Alma 63:5) seems to suggest a large inlet or gulf of the sea “which divides the land”, and “leads into the land northward”, NOT necessarily an isthmus of land which divides the sea and leads to the land northward.
- The given widths of the ‘narrow passes’ mentioned in the Book of Mormon are FAR less than any Mesoamerican Isthmuses. (because of this, traditional Tehantepec models also suggest that the ‘narrow passes’ are not the same as the ‘narrow neck’, but coastal passes on or near it. (Alma 50:34, Alma 52:9, Alma 63:5, Mormon 2&3)
- None of these passes are said to go from ‘the east sea to west sea’. And none are actually mentioned in conjunction with a ‘narrow neck’. Instead, the one north of the city of Bountiful sounds like a spitbar or something extremely narrow with ocean “on the east and on the west” (Alma 50:34), and the other specifies that it goes only from the ‘east unto the west sea‘.
- If the ‘narrow pass’ of Alma 52:9 were an isthmus north of Zarahemla, then the statement regarding fortifying a short section or line of it so the Lamanites cant “harass Zarahemla on every side”‘ makes little sense. It makes far better sense as a narrow coastal pass which is in-line with Zarahemla such as the Xalapa pass of Veracruz, directly east of my model’s Zarahemla.
- If the narrow neck were an isthmus, it seems strange that the city of Bountiful or any other east coast city south of the east narrow pass of Alma 52:9 are not mentioned in regard to Nephite retreat and final battles of Mormon chapters 1-7.
- By far, the best archaeological correlation for the truly urban portrayal of the land of Zarahemla in Book of Mormon times (200 BC to 300 AD) is the Teotihuacan/Cholula area of the Mexican highland. But this region is largely ignored by Book of Mormon geographers because it is NORTH of Mesoamerica’s isthmuses. (see this interview of Michael Coe on Book of Mormon urbanization here)
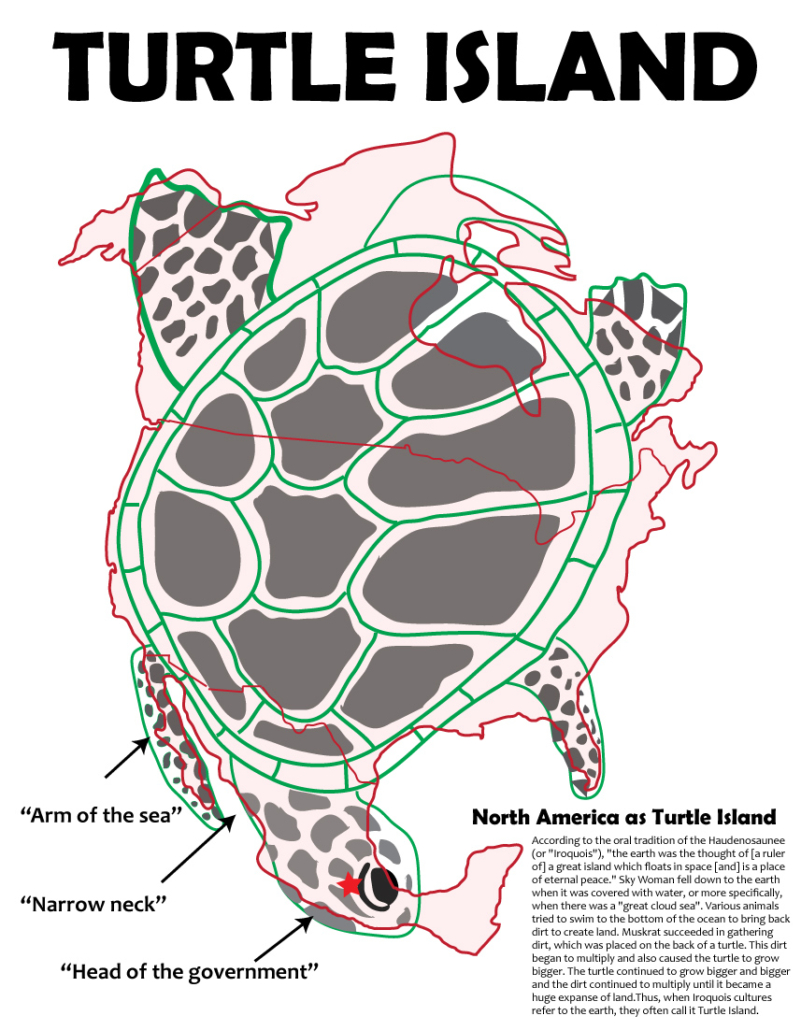
- Early Mesoamerican historians like Ixlilxochitl and other Toltec historians also often mention ancient travel along an “arm of the sea” when describing the Toltec journey from their Land Northward (North America?) to their land Southward (Valley of Mexico). Their descriptions of Baja and the West Mexico Corridor of Xalisco, sound a lot like the Book of Mormon’s Narrow Neck of sea.
.
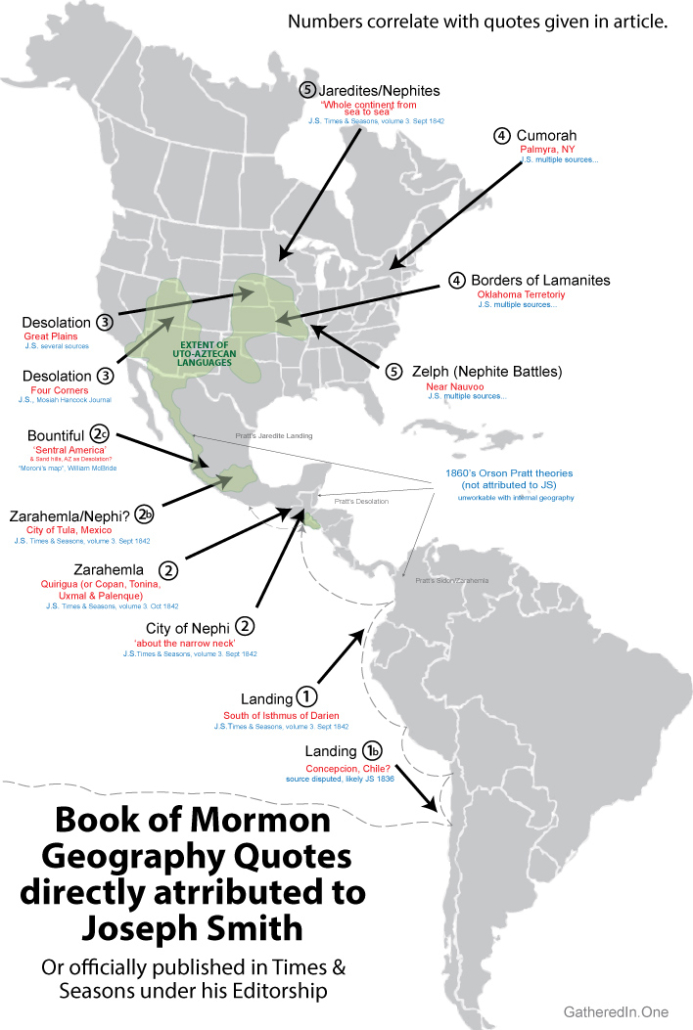
Joseph Smith on the Land of Desolation
On two, and possibly three occurrences, Joseph Smith is directly quoted by a first hand source as stating that the Book of Mormon Land of Desolation extended from the desert Southwest to the Great Plains of North America. This region is of course, one of the more obvious geographical candidates for a region where the text claims the people “did dwell in tents [teepees/wigwams], and in houses of cement [adobe/rock]” because it was one of the only North America desolate desert regions especially having “but little timber” (Hel 3:6–9). It also happens to be directly north of Mexico’s most ‘Bountiful’ population corridor which stretches from Guadalajara through Mexico City to Vera Cruz where more than half of Mexico’s population lives.
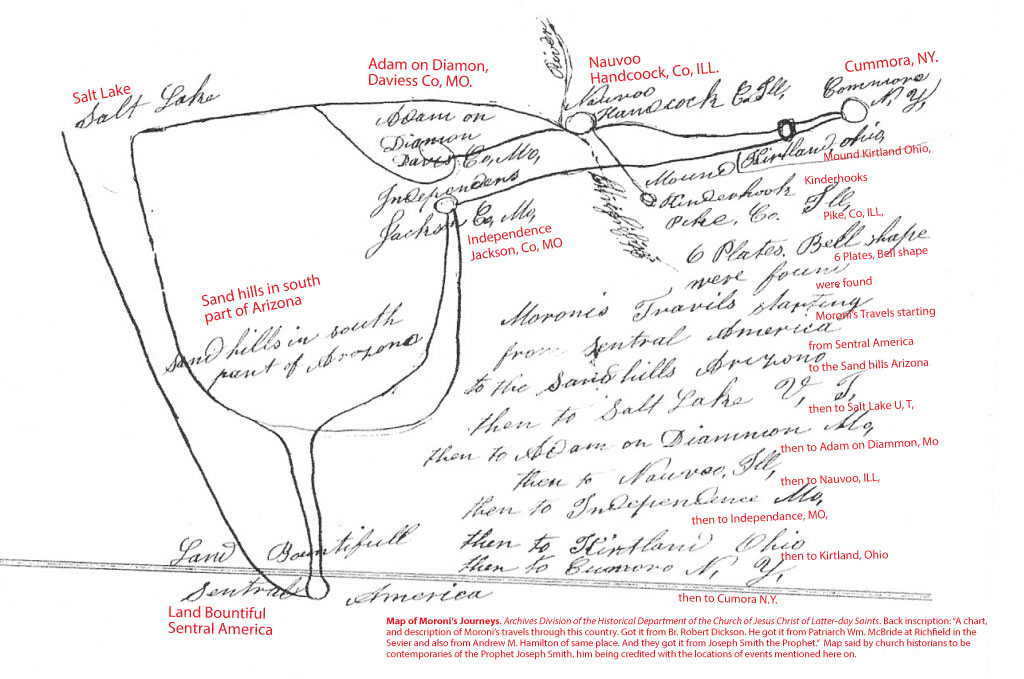
Although of late recounting, Mosiah Hancock gives a first hand account of Joseph Smith saying,
The next day the Prophet came to our home [and said,] ‘Now’, he said, ‘I will show you the travels of this people’. ‘You will build cities to the North and to the South’… ‘and you will have to go to where the Nephites lost their power… Placing his finger on the map, I should think about where Snowflake, Arizona is situated, or it could have been Mexico, he said.’ (Mosiah Hancock, Autobiography, 1834-1865 BYU Special Collections, full account available here. Original)
Levi Hancock, early friend of Joseph, member of Seventy and Council of fifty quotes Joseph Smith as saying to member of Zions Camp that the land of Desolation extended into the Great Plains.
Joseph Smith addressing himself to Sylvester Smith and said, “This is what I told you and now I want to tell you that you may know what I meant. This land [of western Missouri] was called the land of desolation and Onedages was the King and a good man was he. There in that mound did he bury his dead (Autobiography of Levi Hancock (1803-1882), pg. 27 – emphasis added. Original)
Both these quotes fall in line with Joseph’s well known support of a continental model for the Book of Mormon. But since the Book of Mormon clearly states that the Land of Desolation bordered the narrow neck, ONLY a Baja Narrow Neck can makes his model work! (see Alma 22:32–33, Alma 50:34, Alma 63:5)
Nothing in the Book of Mormon actually happens ON the Narrow Neck
It’s somewhat odd that in all the Book of Mormon accounts of occurrences in the Land of Desolation of things happening in association with the ‘narrow neck’, nothing ever happens ON the narrow neck. Instead its always explained as occurring BY the narrow neck. (Likewise the Narrow Passes are never said to be ON the Narrow Neck, but instead only BY it.)
Take Ether 10:20–21 for instance. Many Mesoamerican models attempt to equate the Jaredites almost exclusively with Olmecs living on the isthmus of Tehuantepec. But note the wording of the text for the Jaredite Narrow Neck spoken of in conjunction with Lib’s city. It isn’t built ON the narrow neck of land, but BY the narrow neck of land, BY a place where the sea divides or cuts into the land. (suggesting some kind of deep bay or inlet). And remember, the Jaredite heartland of Moron was said to be near (not on or in) “the land which is called Desolation by the Nephites” (Ether 7:6). It’s not in Bountiful or Desolation, but near Desolation, and Lib’s city is mentioned as if it’s a newly colonized area.
20 And [Lib and his people] built a great city by the narrow neck of land, by the place where the sea divides the land (Ether 10:20)
Does that wording really sound like an isthmus? Or does it sound more like the ‘narrow neck of land’ a geographic identifier representing a truly narrow neck of land / sea inlet like the Sea of Cortez & Baja Peninsula? This reading makes even more sense when we apply it to Alma 63:5 where Hagoth is said to build and launch his boat BY the Narrow Neck and yet still in the borderland of Bountiful near the Land Desolation.
5 …therefore [Haggoth] went forth and built him an exceedingly large ship, on the borders of the land Bountiful, by the land Desolation, and launched it forth into the west sea, by the narrow neck [of sea or land?] which led into the land northward. (Alma:63:5)
Again it’s unclear whether the Narrow Neck here is referring to a narrow neck of ‘land’, as in Ether 10, or a narrow neck of sea, which would actually make more sense given the context of Haggoth launching his boat.
Either way this makes little sense in relation to an isthmus like Tehuantepec, as launching south of it into the West Sea (Pacific) does not really provide much of a shortcut into the ‘land northward’ which is said to be an ‘exceedingly far distance’ and have large bodies of water and homes made of cement for lack of trees (Hel 3:4–11). It does however make a lot of sense if this is talking about the same ‘place where the water divides (cuts into) the land’ of Ether, which provides a travel corridor to take people from the mouth of the Rio Grande de Santiago in West Mexico, up the sea of Coretz to the Colorado River and into the Arizona, New Mexico, Sonora and all the regions of the ancient Puebloan people in the Desert Southwest.
The ‘Narrow Passes’ don’t go from sea to sea and are NEVER said to be ON the Narrow Neck
It’s also interesting to notice that most the time when Mormon speaks of the entire width of the land or region he lived on, he usually uses the descriptive phrase “from east sea to the west sea“
-“divided from the land of Zarahemla by a narrow strip of wilderness, which ran from the sea east even to the sea west…” (Alma 22:27)
-“cover the face of the whole earth, from the sea south to the sea north, from the sea west to the sea east…” (Hel 3:8)
But when he refers to Desolation or Bountiful on the Book of Mormon’s “Narrow Neck”, he only specifically mentions ONE sea. Almost like the ancient author might THINK it’s an isthmus of sorts, but tries to stick to the wording of the maps & texts he’s copying which NEVER clearly say “from the east sea to the west sea” as they did with other parts of the land. Instead its always explained in terms of a pass on only one sea, with an ambiguous reference to the other.
-“distance of a day and a half’s journey for a Nephite, on the line Bountiful and the land Desolation, from the east to the west sea…” (Alma 22:32)
-“fortify against the Lamanites, from the west sea, even unto the east; it being a day’s journey for a Nephite, on the line which they had fortified…” (Hel 4:7)
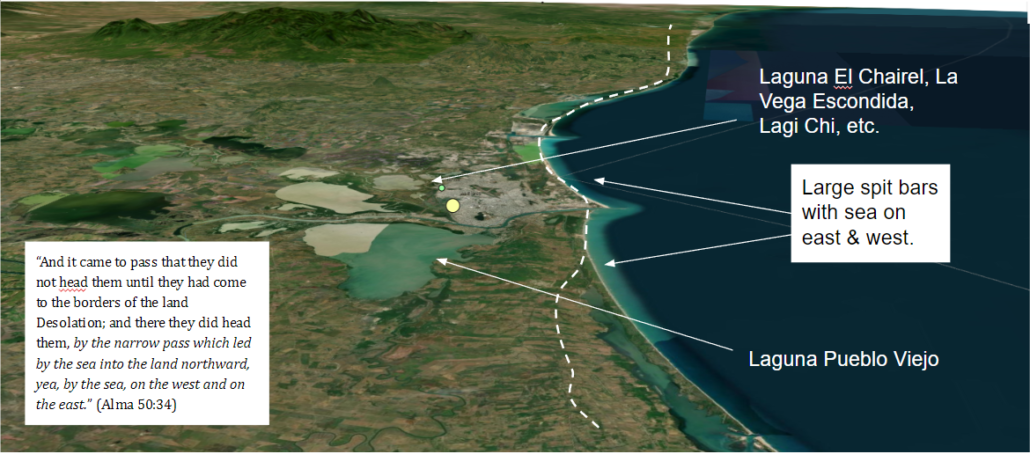
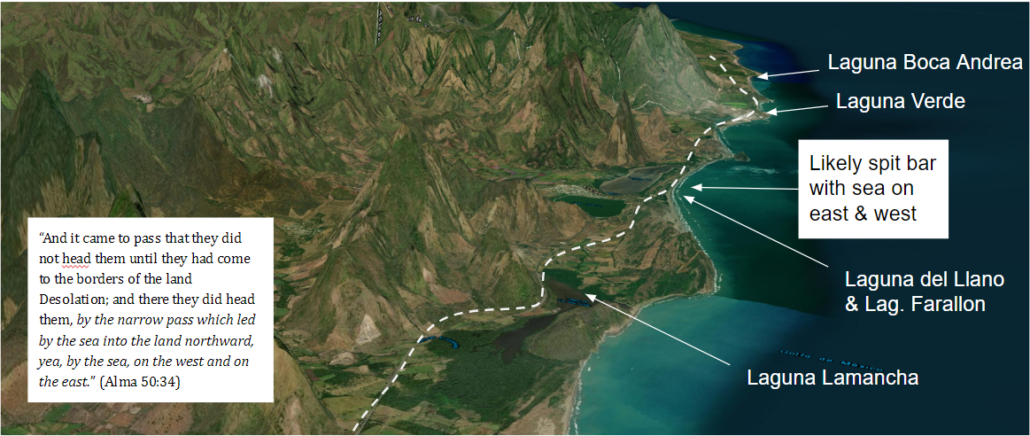
The Eastern ‘pass’ in particular sounds as though it’s more complex than often thought. In Alma 34, a land border dispute between the people of the lands of Lehi & Morianton leads to the people of Morianton’s flight from the southern East Coast to the Land Northward. Although we don’t know how far the people of Morianton made it on their flight northward, we are told that a Nephite army “stops their flight… by the narrow pass which led by the sea… on the west and on the east”. A peculiar wording that seems to suggest an very narrow pass like a passable spit bar or something extremely thin with obvious and visible sea on both the east and west.
34 And it came to pass that they did not head them until they had come to the borders of the land Desolation; and there they did head them, by the narrow pass which led by the sea into the land northward, yea, by the sea, on the west and on the east. (Alma 50:34)
or




.
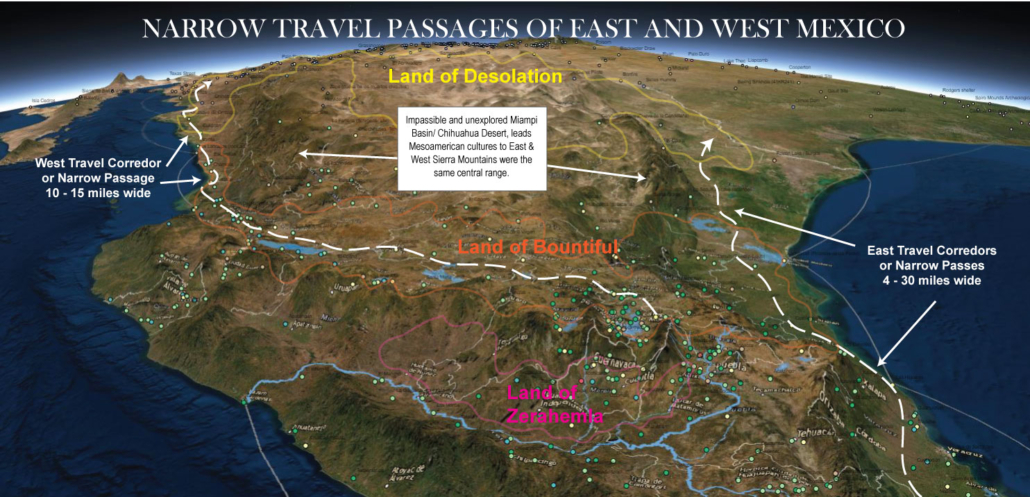
The width of the ‘Narrow Passes’ are FAR less than Mesoamerican Isthmuses
Note that in the two examples of distances given in the Book of Mormon for the width of these passes we have a day or day and a half’s journey. Much as in the works of early Spanish codices transcribers like Ixlilxochitl, distances are always expressed in days instead of linear measurements. And although some debate exists on the distance of a day’s journey, Ixlilxochitl and most scholars place it at around 15 miles. Compare then the day and a half’s journey of Alma 22:32 and the days journey of Hel 4:6–7 (15-27 miles) to the shortest distances across Isthmuses like Tehuantepec (125 miles) or the Isthmus of Guatemala (160 miles) or even the narrowest part of the Isthmus of Darian in Panama (36 miles) and we see the problem with associating the Narrow Neck with these locations.
Even if we suggest the ‘defensive lines of Hel 4:6–7 and Alma 22:32 are simply fortified passes ON the Narrow Neck or Isthmus we still run into a MAJOR problem in all these locations, as NONE of them have defined narrow coastal passes on both sides which are 15-27 miles wide! The Northern coastal plain of Tehuantepec for instance is 50-60 miles wide! (Putting aside the fact that Tehuantepec’s passes face north and south, not east and west as the text suggests.
A place that DOES have easily fortifiable narrow coastal passes which span between the sea and steep mountain chains is northwest and northeast Mexico between the Sierra Madre Occidental, Oriental and the sea. These passes also lie directly north of Mexico’s most agriculturally ‘bountiful’ and populated region and directly south of the Sonoran desert where the landscape turns ‘desolate’, and where Joseph Smith said the land of desolation was!
In my continental model, rather than being oddities, each of these phrases end up being a truly specific description of different aspects of the ‘narrow neck’ area, which I interpret as Baja California, the Gulf of Baja or Sea of Cortez, and the narrow coastal passes between the Sierra Madre Occidental and Oriental and the east and west seas. This interpretation comes not only because it matches perfectly with the archaeology, and is really the only way to make a continental model of Book of Mormon lands which matches with both the text and early LDS prophetic statements. But also from noticing the overwhelming inclusion of the sea of Cortez in the histories and mythologies of the Aztec and other Mesoamerican cultures in the writings of early Aztec/Spanish historians like Ixlilxochtl.
In Modern times we separate the two regions of North America & Mesoamerica by the U.S./Mexican Border and the desolate central Mapimi depression/Chihuahua Desert of North Mexico. However, in both colonial and Book of Mormon times, when nearly all travel was along the West Mexico Coast, the two perhaps were colloquially separated in the minds of natives by Baja and the narrow neck of sea (the sea of Cortez & Baja), which ran parallel to a large desolate region of deserts (desolation).
Summary: all Book of Mormon references to the narrow neck & passes
34 And it came to pass that they did not head them until they had come to the borders of the land Desolation; and there they did head them, by the narrow pass which led by the sea into the land northward, yea, by the sea, on the west and on the east. (Alma 50:34)
9 And he also sent orders unto him that he should fortify the land Bountiful, and secure the narrow pass which led into the land northward, lest the Lamanites should obtain that point and should have power to harass them on every side. (Alma 52:9)
5 And it came to pass that Hagoth, he being an exceedingly curious man, therefore he went forth and built him an exceedingly large ship, on the borders of the land Bountiful, by the land Desolation, and launched it forth into the west sea, by the narrow neck which led into the land northward. (Alma 63:5)
6 And the Nephites and the armies of Moronihah were driven even into the land of Bountiful;
7 And there they did fortify against the Lamanites, from the west sea, even unto the east; it being a day’s journey for a Nephite, on the line which they had fortified and stationed their armies to defend their north country.(Hel 4:6–7)29 And the Lamanites did give unto us the land northward, yea, even to the narrow passage which led into the land southward. And we did give unto the Lamanites all the land southward. (Mormon 2:29)
5 And it came to pass that I did cause my people that they should gather themselves together at the land Desolation, to a city which was in the borders, by the narrow pass which led into the land southward.
6 And there we did place our armies, that we might stop the armies of the Lamanites, that they might not get possession of any of our lands; therefore we did fortify against them with all our force. (Mormon 3:5–6)30 And it bordered upon the land which they called Desolation, it being so far northward that it came into the land which had been peopled and been destroyed, of whose bones we have spoken, which was discovered by the people of Zarahemla, it being the place of their first landing.
31 And they came from there up into the south wilderness. Thus the land on the northward was called Desolation, and the land on the southward was called Bountiful, it being the wilderness which is filled with all manner of wild animals of every kind, a part of which had come from the land northward for food.
32 And now, it was only the distance of a day and a half’s journey for a Nephite, on the line Bountiful and the land Desolation, from the east to the west sea; and thus the land of Nephi and the land of Zarahemla were nearly surrounded by water, there being a small neck of land between the land northward and the land southward.
33 And it came to pass that the Nephites had inhabited the land Bountiful, even from the east unto the west sea, and thus the Nephites in their wisdom, with their guards and their armies, had hemmed in the Lamanites on the south, that thereby they should have no more possession on the north, that they might not overrun the land northward. (Alma 22:32–33)19 …And in the days of Lib the poisonous serpents were destroyed. Wherefore they did go into the land southward, to hunt food for the people of the land, for the land was covered with animals of the forest. And Lib also himself became a great hunter.
20 And they built a great city by the narrow neck of land, by the place where the sea divides the land.
21 And they did preserve the land southward for a wilderness, to get game. And the whole face of the land northward was covered with inhabitants. (Ether 10:20–21)
–
Another possibility: Mormon’s culture believing there to be a ‘Narrow Neck’ in North Mexico
In addition to the above reasoning it seems quite likely that ancient Mesoamericans had a different view of their continents geography than we do. A study of ancient maps and geographies shows that modern LDS Scholars have expected too much from ancient Book of Mormon authors by supposing pre-Columbian cultures had a truly advanced modern-like or google earth understanding of continental geography and shorelines. Indeed, although many ancients understood well the spatial relationships for populated lands & cities, or populated places often traveled, the detailed understanding of uninhabited wildernesses and far-off continental shorelines seems to have been very poor anciently. Especially among cultures without widespread use of nautical navigation technology. And our only indication in both the Book of Mormon text and early Colonial accounts is the wide spread use of Mexico’s west coast to travel between central Mexico and North America (perhaps because of contrary currents and frequent hurricanes which were so dangerous and common on the east coast?)
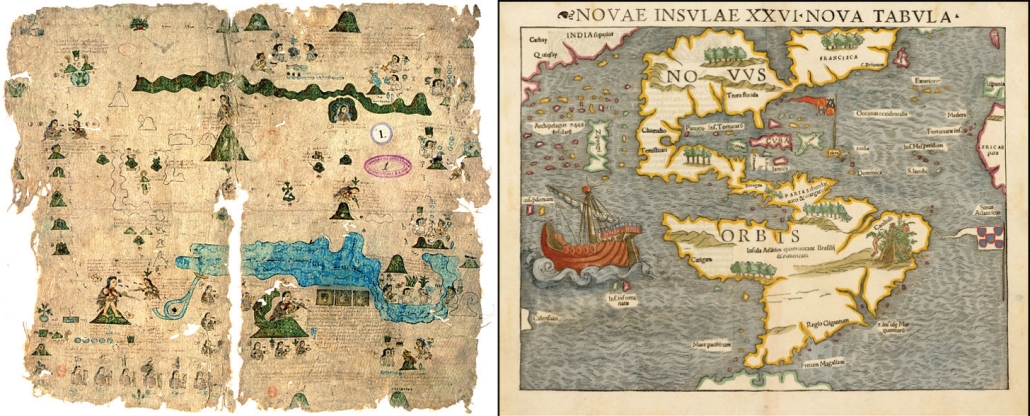


To see a full catalogue of known Mesoamerican cartographic or map representations read "Mesoamerican Cartography" by Barbara Mundy or "The origins and development of the cartographic tradition in the central Mexican highlands" by Chris Helmke
Is Pánuco a Huestec Word for Bountiful?
Our model proposes that much like Sabastian Munster’s early map of the New World (featured above), Book of Mormon authors may have thought there to be another ‘narrow neck’ between the narrow coastal ‘passes’ of Northern Mexico. A misunderstanding likely caused by a belief that the Eastern and Western Sierra Madre mountain ranges were one and the same range. An easy mistake to make given their lack of travel through the nearly impenetrable and uninhabited Mapimi Basin of the Chihuahua Desert. Indeed historical texts show that essentially ALL ancient travel & trade, occurred along the ‘narrow passes’ between the coasts and the steep mountain ranges, with only a few sparsely inhabited mining communities existing in the Deserts of the northern interior.
This seems to have been the belief of the earliest Spanish explorers, likely as suggested to them by their guides. In fact Nuño de Guzmán, one of the first Spanish conquistadors named one of his early west coast cities ‘Pánuco’, naming it after the city with the same name on the east coast! He also founded a Panuco in Durango and another in Zacatecas. Apparently, he had thought the region to be much narrower and named the cities after a conceived coast-to-coast’ region exactly as I propose the Book of Mormon people’s did!
Guzmán was an able and even brilliant lawyer, a man of great energy and firmness, but insatiably ambitious.. he served successively as governor of Pánuco [Sinaloa] (Ibarra, p.22)
… and conceived the idea of extending his conquests to the province of Púnuco [Veracruz] and forming a kingdom extended from coast to coast, from the Gulf of Mexico to the South Sea [Pacific Ocean], which would completely border the New Spain of Hernán Cortés; however, the exploration of Gonzalo López showed that for the moment this project was not feasible… Gonzalo López, crossed the mountain range and reached the northern plateau in the territories of what is now Durango, but, according to the stories, he only found uninhabited lands and “wild” Indians fleeing from the passing of the Spanish… (The conquests of Nuno de Guzman, 1999, Fideicomiso, Historia de las Americas)
In my research I haven’t been able to find any reliable etymology for the name Pánuco (sometimes spelled Pánuco in old texts). But if most Mexican cities and geographic features are either named after Spanish cities or surnames or are transliterations of native words, and Pánuco is NOT a Spanish city or surname. Leaving me to speculate whether Guzman or Ibarra got both the name and idea of Pánuco running sea to sea from the natives!
[add illustration here with location of the four sea-to-sea cities of Panuco on a map, with river Panuco]
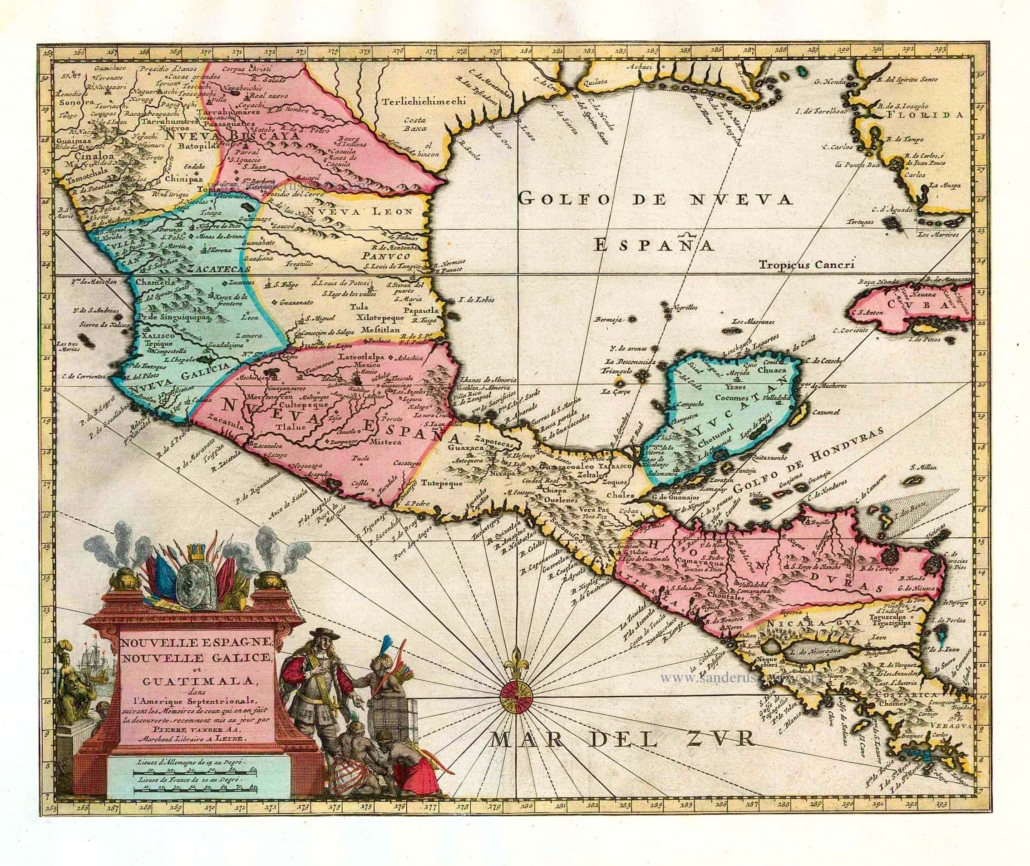
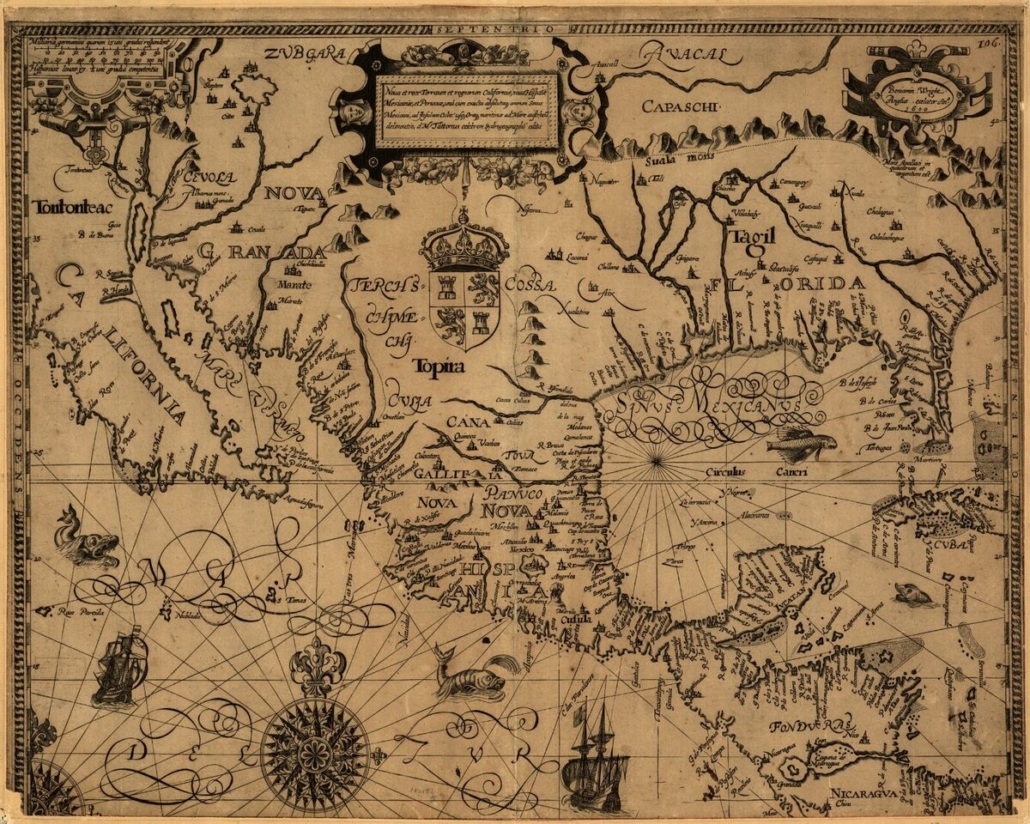
A few more examples of ancient maps, and how even among people’s with advanced writing and sea trade, knowledge of coastal geometries was rudimentary. Especially concerning areas where few lived or traveled.
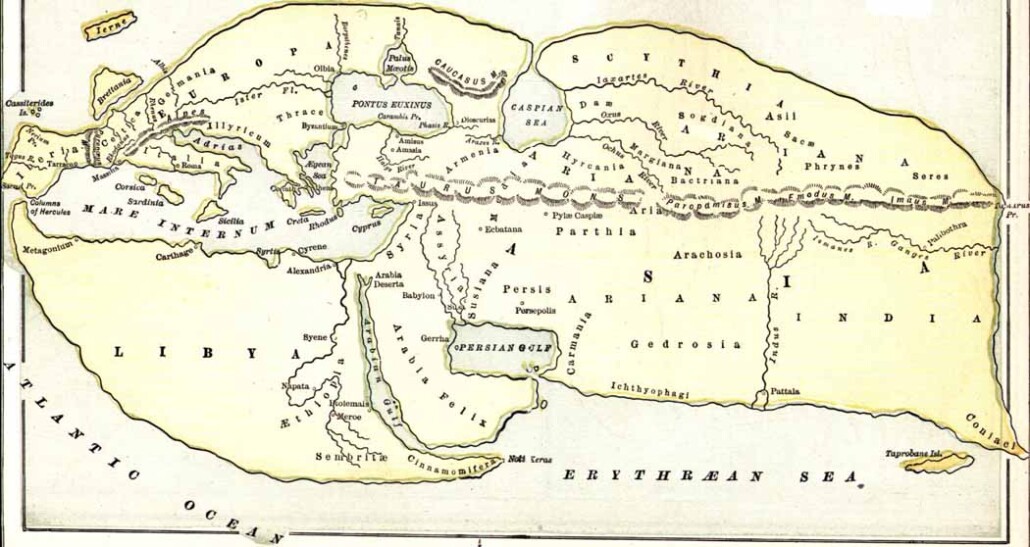
The Turin Papyrus Map is an ancient Egyptian map, generally considered the oldest surviving map of topographical interest from the ancient world. It is drawn on a papyrus reportedly discovered at Deir el-Medina in Thebes. The map shows a 15-kilometre stretch of Wadi Hammamat and has depictions of this wadi’s confluence with wadis Atalla and el-Sid, the surrounding hills. The map contradicts the Sorenson model hypothesis which suggests that Egyptians has a coordinate system rotated 90 degrees.

Surrounded by Water
Interestingly, the native word for the mexican highland and particularly the narrow highland of west-central mexico or valley of Mexico could actually be related to the concept spoken of in Alma 22:32 where it states, “…and thus the land of Nephi and the land of Zarahemla were nearly surrounded by water, there being a small of land between the land northward and the land southward.”
Although often translated as “close to water” or “next to water” and referring solely to the Valley of Mexico, when preceded by ‘Cem’ Ānáhuac is also thought to mean, “surrounded by water”. Cem Ānáhuac is a composed náhuatl name, consisting of the words “cem” (totally) and “Ānáhuac”, in turn a composed word from “atl” (water) and “nahuac”, a location prefix that can also mean “surrounded “. The name can then literally be translated as “land completely surrounded by water “, or “[the] whole of [what is] beside the waters”. See wikipedia links in text above and the Nahuatl dictionary for details.
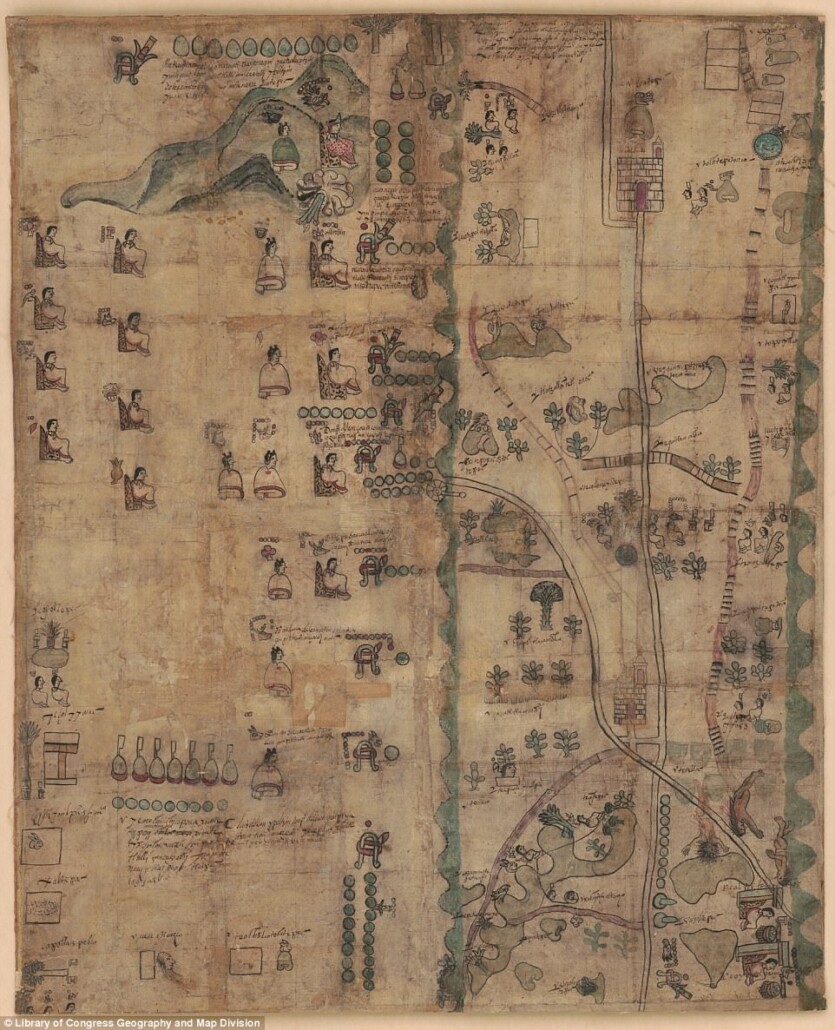
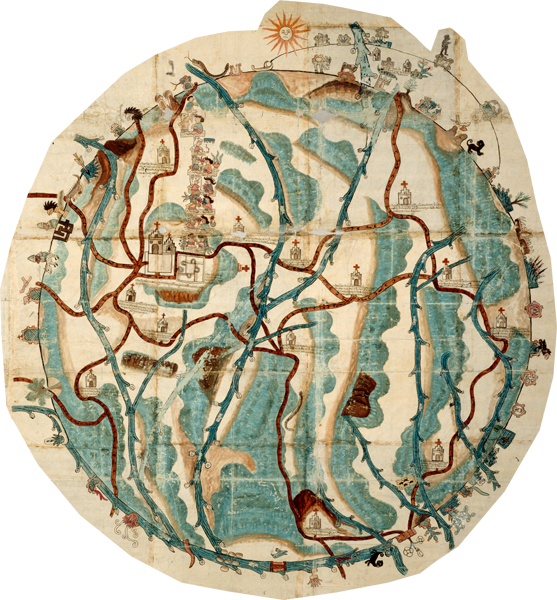
The Mapa de Teozacoalco, painted on twenty-three sheets of European paper pasted together at their edges, contains indigenous pictorial styles, but shows some European influence. The landscape, for instance, is dotted with new Christian churches. Roads show not only human footprints but also horseshoe prints. Emphasis resides in the history of Teozacoalco, with information about a tenth-century ruling family, and subsequent genealogy through the sixteenth century. The circular shape is worthy of special attention. The circle includes 46 glyphic placenames on the community’s territorial boundaries. The extra curve with glyphic placenames refers to an earlier set of boundaries. Alfonso Caso published a small book-length study of this pictorial map (1949, 1992), and Stephen L. Whittington has also published “The Mapa de Teozacoalco: An Early Colonial Guide to a Municipality in Oaxaca,” in The Society for American Archaeology (SAA) Archaeological Record 3:4 (2003), 20–22, and a report on the FAMSI website (http://www.famsi.org/reports/01032/section01.htm). Some of the information in this introduction comes from Barbara E. Mundy, “Mesoamerican Cartography.” In: The History of Cartography, vol. 2.3, David Woodward and G. Malcolm Lewis, eds. 183–256. Chicago and London: University of Chicago Press, 1998. The lead scholar on this close study of the Mapa de Teozacualco is Bas van Doesburg. (Stephanie Wood)

Note the words of Eugene Bolten in his book, Spanish exploration in the Southwest, 1542-1706. Where he notes it was not until at least 1687 that the Spanish fully prove Baja California was a Peninsula and not an island.
Arriving at his destination in 1687, [Father Kino] at once established the mission of Nuestra Senora de los Dolores… over a hundred miles south of Tucson. This mission was his headquarters for twenty- four years of exploration, missionary work, and writing. several times explored the Gila River; and in an attempt to answer the old question whether Califomia was an island or a peninsula…This inquiry was one of the chief interests of the last eleven years of his life, and, as a result of his explorations, he answered it to his own satisfaction in a treatise, as yet unpublished, I believe, which he called ” Cosmographical Demonstration that Califomia is not an Island but a Peninsula, and that it is continuous with this New Spain, the Gulf of Califomia ending in latitude thirty-five degrees
Spanish exploration in the Southwest, 1542-1706, Herber Eugene Bolton.
In this same book nearly the exact same language used in the Book of Mormon is used to describe the Baja California Peninsula.
This enterprise failing, [Father Kino] returned to Mexico and secured permission to work on the mainland opposite the Peninsula, [ie. by the narrow neck] which he had visited while in California. His request was that he might work among the Guaymas and Seris, but he was sent to Pimerfa Alta instead. (ibid)
.
The Uninhabited Zone (and Camino Real Misunderstandings)
The ancient “Camino Real de Tierra Adentro” did NOT extend to Mexico city. This is a myth propagated by Wikipedia and some badly researched articles & maps. That route was only established as a major thoroughfare and used by the Spanish AFTER the railroad came in the 1800s. ALL known accounts of the earliest native or Spanish travelers went along the coast through Chametla, Culiacán and Mochicahui. Interior cities (mines) like Durango and Santa Barbara were reached from the coast. The mines, many which were discovered and founded in the sixteenth century, were serviced by roads coming through the Sierra Mountains and to the coast, NOT through the interior to New Mexico or Mexico City. If you’ve ever driven the interior road, you know why. There are too many long stints in the interior with literally ZERO water. That’s why there’s not a single significant archaeological site in the interior spanning from Mochicahui/La Ferreria to the Cuarenta Casas/Paquime area. Cortez, Coronado, & Frey Macos, de Iberra, they ALL traveled along the coast. The interior route was impassible until Spanish deep-well technology could establish ‘paraje’ stations. This is most obvious by just comparing the ‘founding date’ of coastal regional centers like Culiacán (founded in 1531) to inland cities along the current inland highway like Chihuahua (founded 1709) or Torreón (founded in 1893).
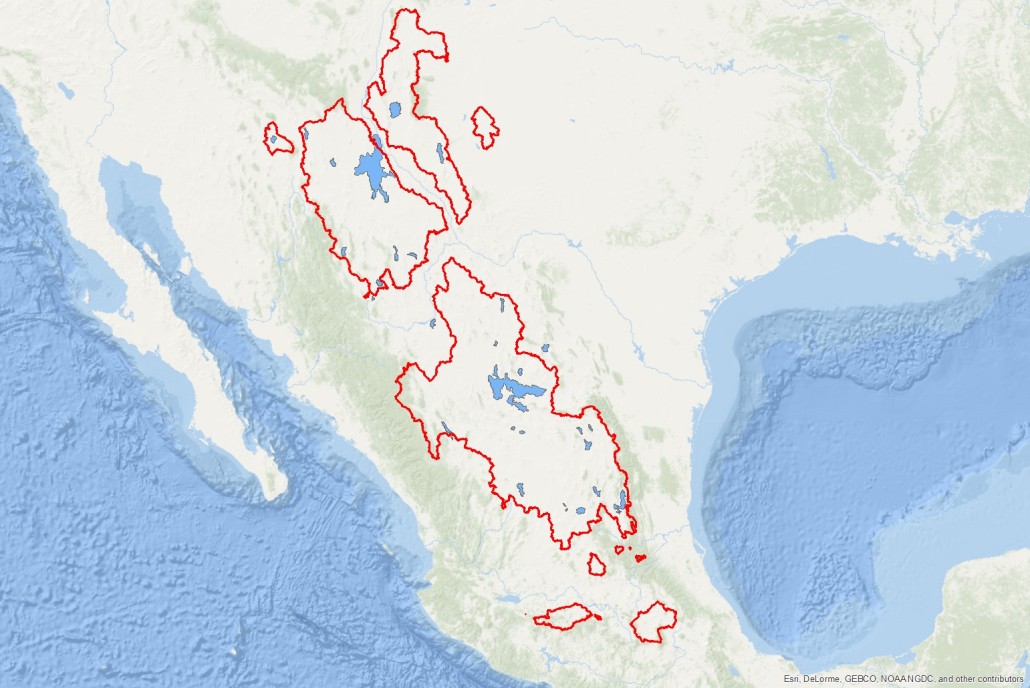
Red outlines show Mexico’s huge closed basins (endorheic basins). These large, sparsely inhabited, desert regions have no outlet to the sea, and drain internally into large ephemeral lakes and desert playas. Settlement and travel through these regions seems to have been extremely rare anciently.

Other considerations
Verse by Verse Analysis To References of the Narrow Neck
The Narrow neck, pass or defensive line mentioned as one of the most prominent geographic features of the Book of Mormon has proved to be incredibly enigmatic. Far greater than the problems of King James Isaiah, Pauline language parallelisms, anachronistic metals or European animals in the Book of Mormon (which can generally be explained by proposing differing manners of dynamic equivalence translation and channeling processes), the narrow neck problem can almost seem insurmountable. Attempts to correlation the Panama Isthmus with the Book of Mormon gain few supporters for reasons that have been described elsewhere (ref). Perhaps the most supported theory of correlating the Isthmus of Tehuantepec with the Book of Mormon’s “narrow pass” has its own difficulties. Foremost of these is the fact that this model forces both the Nephite and Lamanite lands to be in historical Mayan territories. In these model’s Zarahemla (and the entire Nephite culture) are correlated with mundane Mayan cities which bear essentially no early cultural differences from their surrounding peoples (Lamanites)! Additionally these models require the Jaredites (Olmec) to pass writing to the Lehites (Maya) instead of the other way around as described in the Book of Mormon text. The political and religious dominance of the Epi-olmec and Mexican Highland cultures spanning from the formative to the classic are a far better match (and perhaps the only truly plausible match) with what the Book of Mormon narrative depicts of the Nephite/Lamanite religious and political rivalry..
| Reference | wording | sea west mentioned? | sea east mentioned? | days jour-ney | directional indicators |
| Alma 22:32–33 | “small neck of land” or “the line Bountiful” | yes | possibly | 1.5 | from the east to the west sea |
| Alma 50:34 | “the narrow pass” | yes | separately | by the sea, on the west and on the east | |
| Alma 52:9 | “the narrow pass” | no | |||
| Alma 63:5 | “the narrow neck” | yes | no | the west sea | |
| Hel 4:6–7 | “the line” | yes | possibly | 1 | from the west sea, even unto the east |
| Mormon 2:29 | “the narrow passage” | no | |||
| Mormon 3:5–6 | “the narrow pass” | no | |||
| Ether 10:20–21 | “narrow neck of land” | inferred | inferred | place where the sea divides the land |
Available literature in Joseph Smith’s day clearly called the Isthmus of Panama a “narrow neck” (see here for instance), But also, made clear that its distance was more than the “day” (ref) or “day and a half” (ref) mentioned in the Book of Mormon. its curious then that if Joseph or some contemporary wrote the Book of Mormon, they would represent the geography SO horribly. Letter from Balboa dated January 20, 1513. “The Indians state there is another ocean 3 days journey from here… they say the other ocean is very suitable for canoe traveling is always calm…” (reference here)
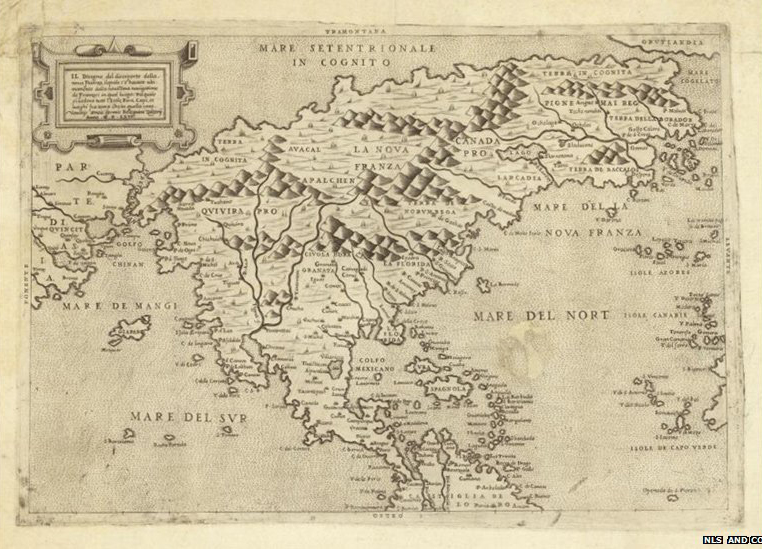
This map from 1566 is one of the oldest printed maps of North America. Created by Paolo Forlani, the first edition was published in 1565. This is one of the first maps to show the Bering Strait – here called the Strait of Anian. It was an educated guess, as it was not discovered until 1648. Like many ancient maps, the geography is a very rough rendition of the true landscape. High quality version available here.
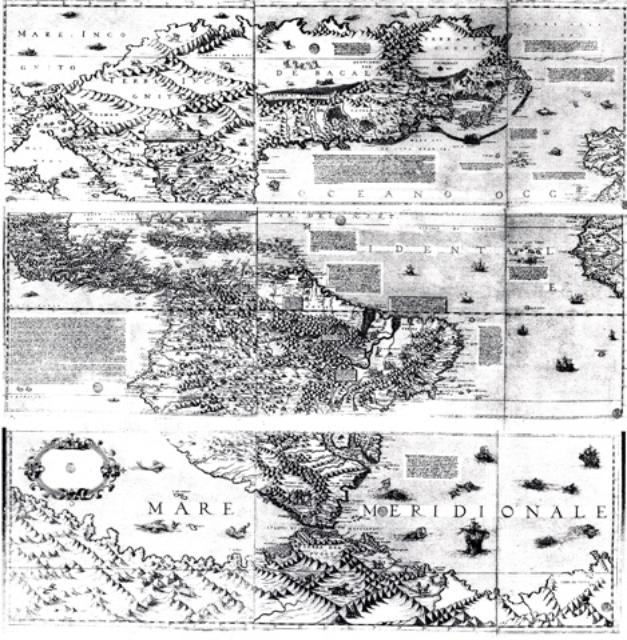
1569 Camocio Map. Several maps associate tolm or ‘tollan’ with Teguayo. Tolm is generally found in the present-day U.S. Southwest on 1500s-1600s era maps. Several maps, including the 1569 Camocio map, show its full spelling as Tolman, which is likely a variation of the Toltec homeland ‘tollan’. See here and here for a similar but higher quality version.
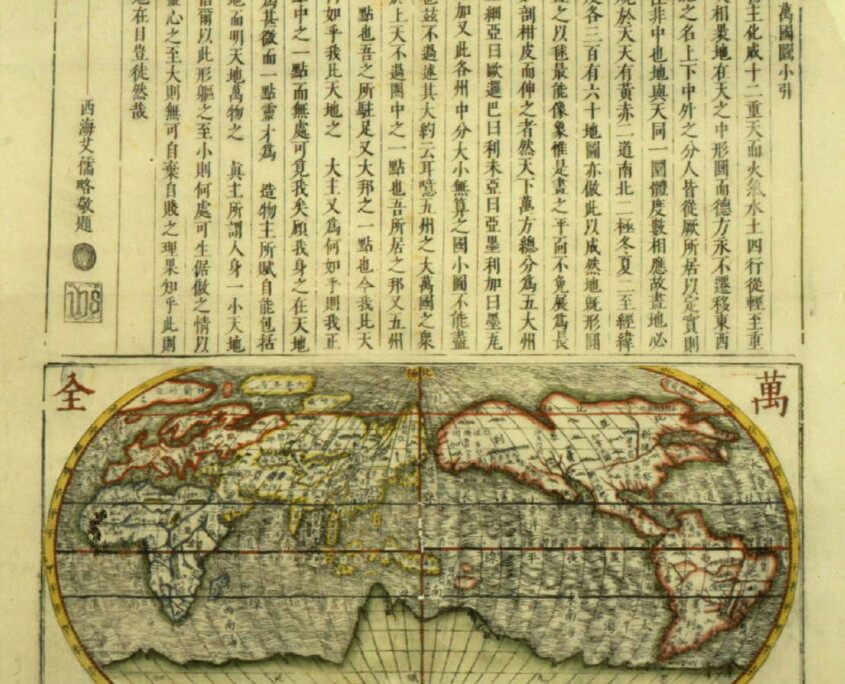
1620s Wanguo Quantu map, by Giulio Aleni, whose Chinese name (艾儒略) appears in the signature in the last column on the left, above the Jesuit IHS symbol.
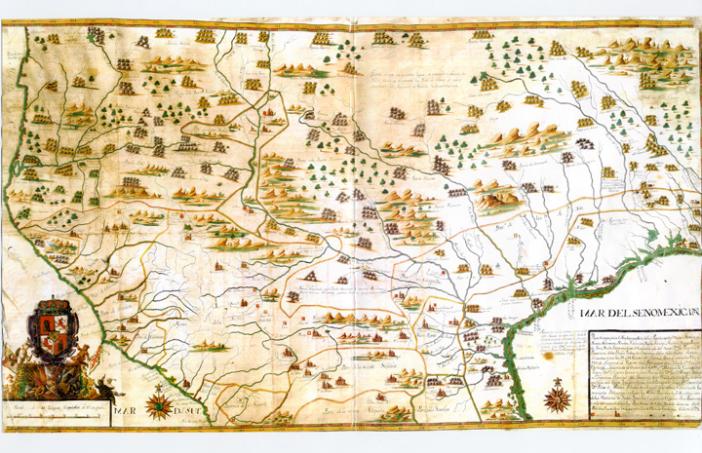
1728 Barreiro Map This is the oldest post-Columbian map which depicts the four migration points of ancient Mexican Indians found in later maps. Some sources also point to this region as a former home for people from Central and South America. See here for an ultra high quality version.
SEE SEVERAL MORE HIGH QUALITY EARLY MAPS OF MEXICO AND THE AMERICAS HERE.